Parijat Thermal Oxidizer, VOU, VDU System
NGSH-0724
Introduction:
A thermal oxidizer is a device used to oxidize hazardous air pollutants (HAPs) by burning them at high temperatures. The thermal oxidizer is a pollution control device with a combustion chamber in which the pollutants are burned with the aid of an oxidizing gas (usually air). The thermal oxidizer uses the heat generated from the oxidation reaction to recover some of the energy that would otherwise be lost. Thermal oxidizers are used in many industrial processes to reduce emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), hazardous air pollutants (HAPs), and other organic compounds. Thermal oxidizers can be used in a variety of applications, including petrochemical, chemical, pharmaceutical, metalworking, and food processing.
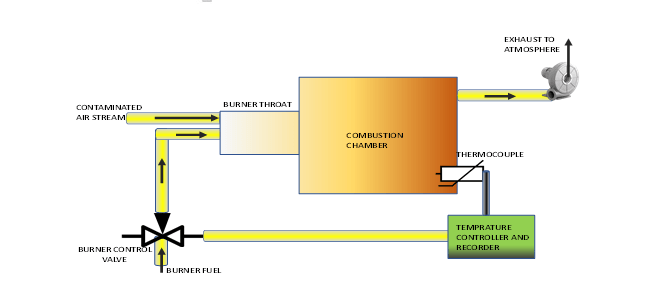
Working of Thermal Oxidizer
Thermal oxidiser works by burning fuel and air to create a high temperature flame. This flame is used to oxidise hazardous pollutants, converting them into less hazardous or non-hazardous compounds such as carbon dioxide and water. The combustion process also generates heat, which is then used to preheat the incoming pollutants prior to oxidation. This helps to increase the efficiency of the process.
Parijat Thermal Oxidizer, VOC, VDC, NGSH-0724 a software for controlling, monitoring a Thermal Oxidizer, Vapor Combustor Unit or Vapor Destruction Unit. It is a sequential
Types of Thermal Oxidizer
Parijat Thermal Oxidizer, VOC, VDC, NGSH-0724 is congruent with all the four distinct types of oxidizers that are listed below.
1. Regenerative Thermal Oxidizers (RTOs)
2. Catalytic Oxidizers
3. Direct Fired Thermal Oxidizers
4. Recuperative Thermal Oxidizers
Spotlights
- Supports a wide range of PLCs.
- Configurable PLC logic for each step
- Long-term history storage, viewing of events & reports.
- Can interface to other systems to exchange data.
- Temperature control: maintains the temperature of the thermal oxidizer within a specified range to ensure that it is operating at its optimal efficiency.
- Gas flow control: regulates the flow of gases into the thermal oxidizer to ensure that it is working at its optimal capacity.
- Emissions monitoring: the emissions from the thermal oxidizer to ensure that they are within acceptable limits of permits and/or regulatory agencies.
- Safety controls: protect against overheating, fires, and other hazards.
Some of the above features may require Hardware options & custom development.



